DESCRIPTION
This is a severe, persistent nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. It is more extreme than morning sickness.
SYMPTOMS
-nausea that does not go away
-vomiting several times everyday
-dehydration
-reduced appetite
-feeling faint or fainting
-weight loss
TREATMENT
Dry, bland foods and fluids together is the first line of treatment. Sometimes, medicines are prescribed to help nausea. Many women with HG have to be hospitalized so they can be fed fluids and nutrients through a tube in their veins. Usually, women with HG begin to feel better by the 20th week of pregnancy. But some women vomit and feel nauseated throughout all the three trimesters.
Tuesday, 13 October 2015
LIKORIA ( Leucorrhoea)
DESRIPTION
Likoria also known as vaginal discharge is a very common condition that has been experienced by most women of all ages. This is because female genitals are highly prone to infections because they are moist and covered at most times. More over, women always sweat in that area which increases the chances of infections and inflammation.
SYMPTOMS
this can be quite an uncomfortable condition which leads to symptoms such as foul smelling, vaginal discharge, headaches, fatigue, stomach pain and constipation. Most women choose to undergo likoria symptoms treatment in the early stages so that the condition does not get any worse as the symptoms can lead to a lot of embarrassment.
CAUSES
Likoria can be caused by injuries to the vagina, lack of cleanliness, the use of sprays, lubricants or jellies, STI's, contraceptives which causes irritation, infections from bacteria, fungi and other parasites.
TREATMENT
Vaginal discharge can be treated at home by eating ripe bananas on a daily basis, drinking a glass of fresh cranberry juice, applying the pulp of a ripe mango to the vaginal area and waiting for it dry up before washing it away, clean the vaginal area with freshly squeezed lemon juice and water.
Likoria also known as vaginal discharge is a very common condition that has been experienced by most women of all ages. This is because female genitals are highly prone to infections because they are moist and covered at most times. More over, women always sweat in that area which increases the chances of infections and inflammation.
SYMPTOMS
this can be quite an uncomfortable condition which leads to symptoms such as foul smelling, vaginal discharge, headaches, fatigue, stomach pain and constipation. Most women choose to undergo likoria symptoms treatment in the early stages so that the condition does not get any worse as the symptoms can lead to a lot of embarrassment.
CAUSES
Likoria can be caused by injuries to the vagina, lack of cleanliness, the use of sprays, lubricants or jellies, STI's, contraceptives which causes irritation, infections from bacteria, fungi and other parasites.
TREATMENT
Vaginal discharge can be treated at home by eating ripe bananas on a daily basis, drinking a glass of fresh cranberry juice, applying the pulp of a ripe mango to the vaginal area and waiting for it dry up before washing it away, clean the vaginal area with freshly squeezed lemon juice and water.
BLUE WAFFLES
DESRIPTION
This is a disease caused by bacteria that enters the vagina and causes havoc in there. The bacterium causes several painful side effects.
SYMPTOMS
The most common sign of blue waffles is intense burning accompaied by severe itching . If left untreated too long, it can cause the vagina to swell significantly. This causes the vagina to turn color to a shade of purple blue. A woman's discharge will also change and become blue, this will lead to unwanted and unpleasant odor thats so strong it will be noticed by others.
TREATMENT
There currently is not a specific cure for the disease. The doctors evalute personal conditions of patients and decide how to treat them based on the information they find when they receive their test results. Since blue waffles is formed by the same bacteria as several sexually transmitted diseases (STI'S) , combination of medications for other STI'S can be used to treat blue waffles.
This is a disease caused by bacteria that enters the vagina and causes havoc in there. The bacterium causes several painful side effects.
SYMPTOMS
The most common sign of blue waffles is intense burning accompaied by severe itching . If left untreated too long, it can cause the vagina to swell significantly. This causes the vagina to turn color to a shade of purple blue. A woman's discharge will also change and become blue, this will lead to unwanted and unpleasant odor thats so strong it will be noticed by others.
There currently is not a specific cure for the disease. The doctors evalute personal conditions of patients and decide how to treat them based on the information they find when they receive their test results. Since blue waffles is formed by the same bacteria as several sexually transmitted diseases (STI'S) , combination of medications for other STI'S can be used to treat blue waffles.
PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE (PID)
DESRIPTION
This is the inflammation of the genital tract accompanied by fever and lower abdominal pains. It can also be described as an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system namely the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries and inside of the pelvis.
SYMPTOMS
Often there may be no symptoms. When present they include lower abdominal; pain, fever, pain with sex, vaginal discharge or irregular menstruation. When these symptoms are iognored, they may lead to long term complications including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain and cancer.
CAUSES
It is caused by bacteria that spread from the vagina and cervix. Infections by chlamydia and gonorrhea are present in 75% to 90% of cases. Without treatment about 10% of those with a chlamydial infection and 40% of those with a gonorrhea will develop PID. Vaginal douching may also increase the risk.
TREATMENT
There are many different antibiotics that can help treat PID. Some are safe for pregnant women. The type one takes depends on the cause of the infection. One may receive a different treatment if they have gonorrhoea or chlamydia.
This is the inflammation of the genital tract accompanied by fever and lower abdominal pains. It can also be described as an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system namely the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries and inside of the pelvis.
SYMPTOMS
Often there may be no symptoms. When present they include lower abdominal; pain, fever, pain with sex, vaginal discharge or irregular menstruation. When these symptoms are iognored, they may lead to long term complications including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain and cancer.
CAUSES
It is caused by bacteria that spread from the vagina and cervix. Infections by chlamydia and gonorrhea are present in 75% to 90% of cases. Without treatment about 10% of those with a chlamydial infection and 40% of those with a gonorrhea will develop PID. Vaginal douching may also increase the risk.
TREATMENT
There are many different antibiotics that can help treat PID. Some are safe for pregnant women. The type one takes depends on the cause of the infection. One may receive a different treatment if they have gonorrhoea or chlamydia.
MENOPAUSE
DESCRIPTION
Menopause is the time when a woman stops having menstrual periods. Many women experience a variety of symptoms as a result of the hormonal changes associated with the transition of menopause. Most women often loose bone density and their blood cholestrol levels may worsen, increasing their risk of heart diseases. The most common age range at which women experience menopause is 48-55 years.
SYMPTOMS
hot flashes- these are the most common symptoms of menopause. According to some studies, hot flashes occur in as many as 75% of perimenopausal women. Hot flash symptoms may vary among women. Commonly , a hot flash is a feeling of warmth that spreads over the body, lasting from around 30 seconds to a few minutes.
vaginal discharge- because estrogen affect the vaginal lining, perimenopausal women may also have pain during intercourse and may note a change in vaginal discharge.
Breast changes- menopause may cause changes in the shape of the breasts.
Bone loss- rapid bone loss is common during the perimenopausal years. Most women reach their peak bone density when aged 25-30 years. No pain is associated with bone loss.
Cholesterol- cholesterol profiles also change significantly at the time of menopause. Total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels increase. It is associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
CAUSES
Menopause occurs due to a complex series of hormonal changes. Associated with menopause is a decline in the number of functioning eggs within the ovaries. At the time of birth, most females have about 1-3 million eggs which are gradually lost throughout a woman's life. By the time of a girl's first menstrual period, she has an average of about 400 000 eggs. By the time of menopause a woman may have about 10 000 eggs. Estrogen affects many parts of the body including the blood vessels , heart, bones, breasts, uterus, urinary system, skin and brain. Loss of estrogen is believed to be the cause of many of the symptoms associated with menopause. At the time of menopause, the ovaries also decrease their production of testestrone- a hormone involved in libido sexual drive.
TREATMENT
Menopause itself is a hormonal part of life and not a disease that requires treatment. However, treatment of associated symptoms is possible if these become substantial or severe.
Hormone therapy(HT) / Hormone replacement therapy consists of estrogens or a combination of estrogens and progesterone. Hormone therapy has been used to control the symptoms of menopause related to declining estrogen levels such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness and HT is still the most effective way to treat these symptoms.
Menopause is the time when a woman stops having menstrual periods. Many women experience a variety of symptoms as a result of the hormonal changes associated with the transition of menopause. Most women often loose bone density and their blood cholestrol levels may worsen, increasing their risk of heart diseases. The most common age range at which women experience menopause is 48-55 years.
SYMPTOMS
hot flashes- these are the most common symptoms of menopause. According to some studies, hot flashes occur in as many as 75% of perimenopausal women. Hot flash symptoms may vary among women. Commonly , a hot flash is a feeling of warmth that spreads over the body, lasting from around 30 seconds to a few minutes.
vaginal discharge- because estrogen affect the vaginal lining, perimenopausal women may also have pain during intercourse and may note a change in vaginal discharge.
Breast changes- menopause may cause changes in the shape of the breasts.
Bone loss- rapid bone loss is common during the perimenopausal years. Most women reach their peak bone density when aged 25-30 years. No pain is associated with bone loss.
Cholesterol- cholesterol profiles also change significantly at the time of menopause. Total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels increase. It is associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
CAUSES
Menopause occurs due to a complex series of hormonal changes. Associated with menopause is a decline in the number of functioning eggs within the ovaries. At the time of birth, most females have about 1-3 million eggs which are gradually lost throughout a woman's life. By the time of a girl's first menstrual period, she has an average of about 400 000 eggs. By the time of menopause a woman may have about 10 000 eggs. Estrogen affects many parts of the body including the blood vessels , heart, bones, breasts, uterus, urinary system, skin and brain. Loss of estrogen is believed to be the cause of many of the symptoms associated with menopause. At the time of menopause, the ovaries also decrease their production of testestrone- a hormone involved in libido sexual drive.
TREATMENT
Menopause itself is a hormonal part of life and not a disease that requires treatment. However, treatment of associated symptoms is possible if these become substantial or severe.
Hormone therapy(HT) / Hormone replacement therapy consists of estrogens or a combination of estrogens and progesterone. Hormone therapy has been used to control the symptoms of menopause related to declining estrogen levels such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness and HT is still the most effective way to treat these symptoms.
Tuesday, 6 October 2015
OVARIAN CANCER
DESCRIPTION
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovary. It results in the abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body.
SYMPTOMS
When this process begins, symptoms may be vague or not apparent but they become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms include bloating, pelvic pain and abdominal swelling among others.
CAUSES
Its not clear what causes ovarian cancer. In general, cancer begins when a generic mutation turns normal cells into abnormal cancer cells. Cancer cells quickly multiply, forming a tumor. They can invade nearby nearby tissues and break off from an initial tumor to spread elsewhere in the body.
TYPES OF OVARIAN CANCER
The type of cell where the cancer begins determines the type of ovarian cancer you have. They include
EPITHELIAL TUMORS which begin in the thin layer of tissue that coves the outside of the ovaries. About 90% of ovarian cancers are epithelial.
GERM CELL TUMORS which begin in the egg producing cells. These rare ovarian cancers tend to occur in younger women.
TREATMENT
Surgery is the initial treatment of choice for ovarian cancer, provided patients are medically fit. It can also be treated by chemotherapy and radiation can also be used depending on the stage of the disease.

Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovary. It results in the abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body.
SYMPTOMS
When this process begins, symptoms may be vague or not apparent but they become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms include bloating, pelvic pain and abdominal swelling among others.
CAUSES
Its not clear what causes ovarian cancer. In general, cancer begins when a generic mutation turns normal cells into abnormal cancer cells. Cancer cells quickly multiply, forming a tumor. They can invade nearby nearby tissues and break off from an initial tumor to spread elsewhere in the body.
TYPES OF OVARIAN CANCER
The type of cell where the cancer begins determines the type of ovarian cancer you have. They include
EPITHELIAL TUMORS which begin in the thin layer of tissue that coves the outside of the ovaries. About 90% of ovarian cancers are epithelial.
GERM CELL TUMORS which begin in the egg producing cells. These rare ovarian cancers tend to occur in younger women.
TREATMENT
Surgery is the initial treatment of choice for ovarian cancer, provided patients are medically fit. It can also be treated by chemotherapy and radiation can also be used depending on the stage of the disease.

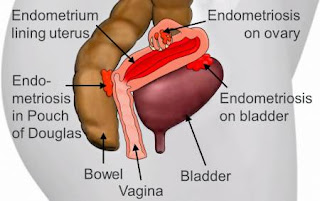
ENDOMETRIOSIS
DESCRIPTION
This is a condition that results from the appearance of endometrial tissue that normally grows inside the uterus grows outside the womb and causing pelvic pain especially associated with menstruation.
SYMPTOMS
Some women with endometriosis do not have symptoms. Other women have symptoms ranging from mild to severe. The symptoms include pelvic pain, severe menstrual cramps, pain during sex, rectal pain, abnormal bleeding, blood satins in the urine or stools and infertility. symptoms are usually most severe before or during menstrual period. Other conditions such as uterine fibroids and adenomyosis can cause symptoms similar to endometriosis.
TREATMENT
Although surgery does not cure endometriosis, it does offer short term results for most women and long-term relief for a few. Surgery may be recommended when treatment with hormone therapy has not controlled symptoms, and symptoms interfere with daily living and also when endometrial implants or scar tissue interferes with the functions of other organs in the belly. the most common surgery is called laparoscopy..
This is a condition that results from the appearance of endometrial tissue that normally grows inside the uterus grows outside the womb and causing pelvic pain especially associated with menstruation.
SYMPTOMS
Some women with endometriosis do not have symptoms. Other women have symptoms ranging from mild to severe. The symptoms include pelvic pain, severe menstrual cramps, pain during sex, rectal pain, abnormal bleeding, blood satins in the urine or stools and infertility. symptoms are usually most severe before or during menstrual period. Other conditions such as uterine fibroids and adenomyosis can cause symptoms similar to endometriosis.
TREATMENT
Although surgery does not cure endometriosis, it does offer short term results for most women and long-term relief for a few. Surgery may be recommended when treatment with hormone therapy has not controlled symptoms, and symptoms interfere with daily living and also when endometrial implants or scar tissue interferes with the functions of other organs in the belly. the most common surgery is called laparoscopy..
FIBROIDS
DESCRIPTION
Fibroids are noncancerous growths on the uterus that often appear during childbearing years. They are also known as uterine fibroids, myomas or fibromyomas. They can vary in size, from that of a bean to as large as a melon.
SYMPTOMS
Uterine fibroids symptoms can develop slowly over several years or rapidly over several months. Most women with uterine fibroids have mild symptoms to none at all and never need treatment. For some women, fibroids symptoms become a problem. Pain and heavy menstrual bleeding are the most common signs, difficulty in falling pregnant is another sign of fibroids. The type of symptoms women have can depend on where the fibroid is located in the uterus. Other symptoms include painful periods, bleeding between periods, prolonged periods, pelvic pains, pain during sexual intercourse, bloating, urinary problems, miscarriage and infertility.
CAUSES
During a woman's reproductive years, her estrogen and progesterone levels are high. When they are high, especially during pregnancy, fibroids tends to swell. When they are low, fibroids may shrink, e.g during menopause. Fibroids are also hereditary, if there is a history of fibroids in the family, other female members of the family are at a higher risk of developing fibroid.
TREATMENT
Most fibroids are harmless, do nt cause symptoms and shrink with menopause. but some fibroids are painful, press on other internal organs, bleed and cause anemia or pregnancy problems. These complicated fibroids can be surgically removed, the blood supply to these fibroids can be cut off , the entire uterus can be removed, or medicine can temporarily shrink fibroids. The treatment will depend on whether you have severe symptoms or not.
Fibroids are noncancerous growths on the uterus that often appear during childbearing years. They are also known as uterine fibroids, myomas or fibromyomas. They can vary in size, from that of a bean to as large as a melon.
SYMPTOMS
Uterine fibroids symptoms can develop slowly over several years or rapidly over several months. Most women with uterine fibroids have mild symptoms to none at all and never need treatment. For some women, fibroids symptoms become a problem. Pain and heavy menstrual bleeding are the most common signs, difficulty in falling pregnant is another sign of fibroids. The type of symptoms women have can depend on where the fibroid is located in the uterus. Other symptoms include painful periods, bleeding between periods, prolonged periods, pelvic pains, pain during sexual intercourse, bloating, urinary problems, miscarriage and infertility.
CAUSES
During a woman's reproductive years, her estrogen and progesterone levels are high. When they are high, especially during pregnancy, fibroids tends to swell. When they are low, fibroids may shrink, e.g during menopause. Fibroids are also hereditary, if there is a history of fibroids in the family, other female members of the family are at a higher risk of developing fibroid.
TREATMENT
Most fibroids are harmless, do nt cause symptoms and shrink with menopause. but some fibroids are painful, press on other internal organs, bleed and cause anemia or pregnancy problems. These complicated fibroids can be surgically removed, the blood supply to these fibroids can be cut off , the entire uterus can be removed, or medicine can temporarily shrink fibroids. The treatment will depend on whether you have severe symptoms or not.
Sunday, 4 October 2015
OVARIEN CYSTS
DESCRIPTION
These are closed, sac like structures within the ovary that are filled with a liquid / semi-solid structure. A cyst is merely a general term used for a fluid-filled structure which may or may not represent a tumor or new growth.
CAUSES
Ovarian cysts form for numerous reasons. The most common type is a follicular cyst, which results from the growth of a follicle. A follicle is the normal fluid-filled sac that contains an egg. Follicular cysts form when the follicle grows larger than normal during the menstrual cycle and does not open to release the egg. Usually follicular cysts resolve spontaneously over the course of days to months. they can contain blood from leakage of blood into the egg sac.
Another type of ovarian cyst is a corpus luteum cysts. The corpus luteum is an area of tissue within the ovary that occurs after an egg has been released from the follicle. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum usually breaks down and disappears. It may fill with fluid or blood and persist as a cyst on the ovary. This cyst is usually found on only one side, produces no symptoms and resolves spontaneously.
infections of the pelvic organs can involve the ovaries and fallopian tubes. In severe cases, pus filled cystic spaces may be present on, in or around the ovary or tubes. These are known as tubo-ovarian abscesses. Other types of cysts includes dermoid cysts.
Most ovarian cysts are never noticed and heal without women ever realizing that they are there. When a cyst causes symptoms, pain in the abdomen or pelvis is the most common one. The pain can be caused from rupture of the cyst, bleeding into the cyst, rapid growth and stretching or twisting of the cyst around its blood supply. If a cyst has reached a large size, other symptoms may arise as a result of pressure or distortion of adjacent anatomical structures. They include bloating, indigestion, abdominal fullness, feeling full after eating a small amount of food, urinary urgency or pain with sexual intercourse.
DIAGNOSIS
sometimes ovarian cysts may be noticed by a doctor during bimanual examination of the pelvis. If a cyst is suspected based upon symptoms or physical examination, imaging techniques are used. Most cysts are diagnosed by ultrasound. Ultrasound uses sound waves to produce an image of structures within the body, it is painless and harmless. Cysts can also be detected using other imaging methods such as CT scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
TREATMENT
Oral contraceptives or birth control pills are very helpful to regulate the menstrual cycle, prevent the formation of follicles that can turn into cysts and also reduces the size of an existing cyst. Pain relievers or anti- inflammatory medication such as napacod may help reduce pelvic pain caused by ovarian cysts. Ultrasonic observation or endovaginal ultrasound are used to monitor the growth of the cyst. An ovarian cyst may twist and cause severe abdominal pain as well as nausea and vomiting. this is an emergency where surgery is necessary to correct it.
These are closed, sac like structures within the ovary that are filled with a liquid / semi-solid structure. A cyst is merely a general term used for a fluid-filled structure which may or may not represent a tumor or new growth.
CAUSES
Ovarian cysts form for numerous reasons. The most common type is a follicular cyst, which results from the growth of a follicle. A follicle is the normal fluid-filled sac that contains an egg. Follicular cysts form when the follicle grows larger than normal during the menstrual cycle and does not open to release the egg. Usually follicular cysts resolve spontaneously over the course of days to months. they can contain blood from leakage of blood into the egg sac.
Another type of ovarian cyst is a corpus luteum cysts. The corpus luteum is an area of tissue within the ovary that occurs after an egg has been released from the follicle. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum usually breaks down and disappears. It may fill with fluid or blood and persist as a cyst on the ovary. This cyst is usually found on only one side, produces no symptoms and resolves spontaneously.
infections of the pelvic organs can involve the ovaries and fallopian tubes. In severe cases, pus filled cystic spaces may be present on, in or around the ovary or tubes. These are known as tubo-ovarian abscesses. Other types of cysts includes dermoid cysts.
Most ovarian cysts are never noticed and heal without women ever realizing that they are there. When a cyst causes symptoms, pain in the abdomen or pelvis is the most common one. The pain can be caused from rupture of the cyst, bleeding into the cyst, rapid growth and stretching or twisting of the cyst around its blood supply. If a cyst has reached a large size, other symptoms may arise as a result of pressure or distortion of adjacent anatomical structures. They include bloating, indigestion, abdominal fullness, feeling full after eating a small amount of food, urinary urgency or pain with sexual intercourse.
DIAGNOSIS
sometimes ovarian cysts may be noticed by a doctor during bimanual examination of the pelvis. If a cyst is suspected based upon symptoms or physical examination, imaging techniques are used. Most cysts are diagnosed by ultrasound. Ultrasound uses sound waves to produce an image of structures within the body, it is painless and harmless. Cysts can also be detected using other imaging methods such as CT scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
TREATMENT
Oral contraceptives or birth control pills are very helpful to regulate the menstrual cycle, prevent the formation of follicles that can turn into cysts and also reduces the size of an existing cyst. Pain relievers or anti- inflammatory medication such as napacod may help reduce pelvic pain caused by ovarian cysts. Ultrasonic observation or endovaginal ultrasound are used to monitor the growth of the cyst. An ovarian cyst may twist and cause severe abdominal pain as well as nausea and vomiting. this is an emergency where surgery is necessary to correct it.
BACKGROUND ON WOMEN'S HEALTH
Women's lives have changed over the centuries. Historically, life was particularly difficult for most women. Aside from the numerous dangers and diseases, women became wives and mothers often when they were just emerging from their own childhood. In the past, childbirth itself was risky and not infrequently, this led to the death of the mother. Most women did not live long enough to be concerned about menopause and old age.
GYNAECOLOGY is the primary branch of medical science concerned with women's health issues. The word gynaecology is made up of two words which are "gynaeco" meaning a woman and "logic" meaning knowledge. Combined together its 'woman knowledge", therefore women are ought to know the most important things concerning their health especially female diseases.
GYNAECOLOGY is the primary branch of medical science concerned with women's health issues. The word gynaecology is made up of two words which are "gynaeco" meaning a woman and "logic" meaning knowledge. Combined together its 'woman knowledge", therefore women are ought to know the most important things concerning their health especially female diseases.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)